Photo 1: Jebel Ali Desalination Plant, Dubai, UAE (Source: Georgeekman, Flickr).
Water resources in the UAE can be classified into two main categories: conventional, such as surface water (including aflaj water systems, springs and dams) and groundwater (shallow and deep aquifers), and non-conventional, such as desalinated water, treated wastewater and cloud seeding.
Surface water
The surface water is negligible and includes floodwater, water retained in dams, some very small streams, ponds and spring water. These are either confined or flowing when there are land slopes and are replenished by rainfall or groundwater.
Due to the UAE’s location in a dry belt region, rainfall is limited and floodwaters leak into the ground, especially in sedimentary areas. Thus, it is crucial to build dams to harvest rainwater and store surface water behind them and to help feed the aquifer, although most of it is lost to high evaporation. The average annual surface water flow through wadis (valleys) ranges from 23 million cubic metres (MCM) to 138MCM.[1]
Groundwater
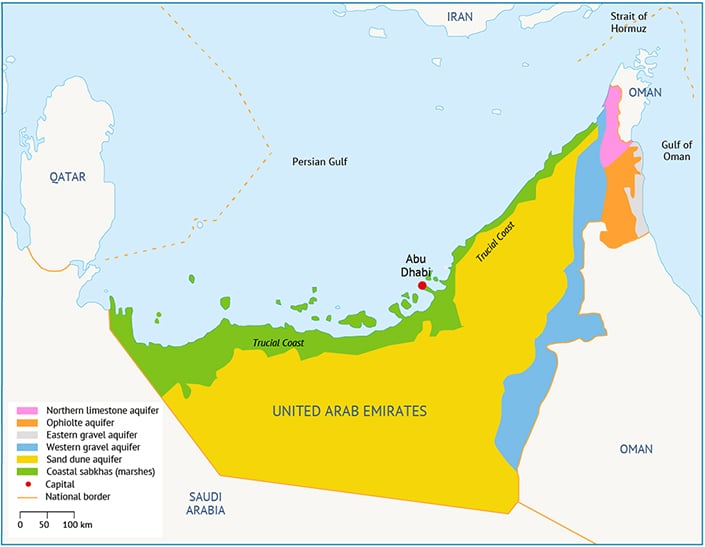
Groundwater is the main natural water resource. The total volume of groundwater is quite significant at around 640 billion cubic metres (BCM), but only 3% of it (around 20BCM) is fresh.
In the UAE’s arid environment, groundwater is an important and precious resource for municipal and rural supplies, environmental protection, and social and economic development. However, most of the groundwater used in the UAE is brackish. Groundwater resources can be divided into renewable (shallow aquifers) and non-renewable resources (deep aquifers).
Groundwater resources occur in the aquifers located in the Bajada region, in the eastern part of the country. The aquifers consist of alluvial fan deposits along the base of the Oman and Ras Al-Khaimah Khaymah mountains that extend over a large area. The upper aquifer is composed of gravel sand and silt, the lower aquifer of limestone, dolomite and marl. Both aquifers range in thickness from 200 to 800 metres. In addition, the Dammam and Umm er-Radhuma aquifers, which extend into the western desert areas, contain highly saline water.
The recharge of shallow aquifers depends mainly on rainfall events and surface run-off, and thus may vary considerably from year to year. Due to the high evaporation rate and surface water run-off in mountain areas, only 10-14% of the total precipitation percolates to recharge the shallow groundwater aquifers.[2]
In recent years, aquifer conditions have improved as a result of measures taken to reduce groundwater abstraction to sustainable levels. However, full recovery will take generations. Controlling the groundwater mining has also commenced, although more steps still needed to reduce the abstraction volume to sustainable levels. In addition, a comprehensive set of measures for sustainable groundwater management have been adopted, notably establishing strong monitoring and regulatory programmes and conserving traditional water systems such as aflaj.
The high evaporation rates during the summer increase the accumulation of salts in the root zone. Excess irrigation water percolates deeply and carries the accumulated salts to the aquifer, further aggravating the problem of groundwater deterioration.
The main aquifer system is shown in Map 1.
Map 1. The main aquifer system in UAE.[3]
Non-conventional water sources
Desalination
In order to meet both the qualitative and quantitative requirements for drinking water standards, domestic water supplies rely mainly on desalinated water (around 99%), which is used either directly or blended with groundwater.
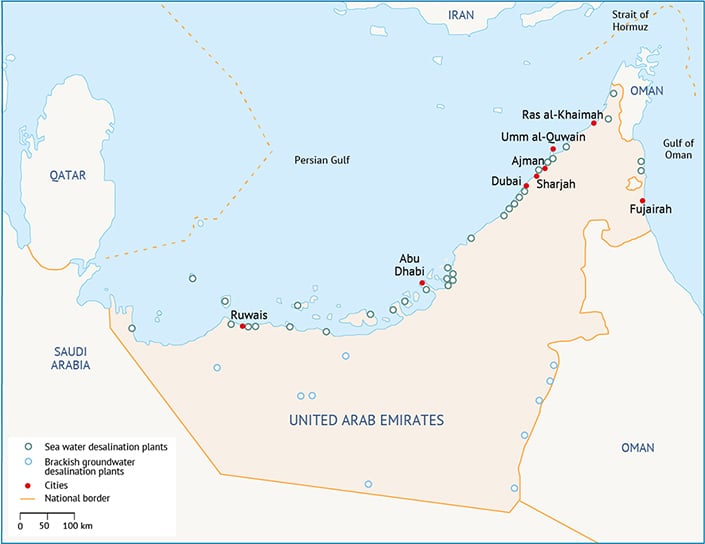
After Saudi Arabia, the UAE has the highest desalination capacity globally.[4] Most of the desalination plants use co-generation multi-stage flash (MSF) technology or multiple-effect distillation (MED), whereas only two plants use reverse osmosis (RO) technology. As of 2015, there are 33 major water desalination plants in the UAE (Map 2).
The availability of desalinated water at relatively low costs may also be an attractive means of meeting industrial water demand, since industries have been willing to pay for water at rates higher than domestic and agricultural rates.
Map 2. Desalination plants in UAE.[5]
Renewable energy can play a key role in lowering the cost of desalinated water. In fact, the UAE is very progressive when it comes to developments and innovations in green technology. Food and water security are important issues for the country, which already imports more than 90% of its food. Furthermore, the UAE aims to increase its total renewable energy by 24% by 2021. The water demand is expected to grow about 30% by 2030, and seawater desalination requires ten times more energy than surface water production.[6]
Treated wastewater
Treated wastewater represents one of the most important alternatives to meet some of the present water requirements and lessen the long-term supply-demand imbalance. Thanks to the completion of wastewater treatment facilities and the expansion of urban sewage networks, large volumes of treated wastewater have become available. Due to environmental considerations, wastewater is treated completely or partially, regardless of its intended use.
At present, the UAE operates modern treatment facilities with tertiary and advanced treatment capabilities. Treated water is used mainly for urban purposes, such as irrigating gardens and highway landscaping. Municipalities are responsible for building and managing sewage systems, creating networks for storm water collection and reusing treated wastewater. However, half of the treated effluents are discharged into the Arabian Gulf. The main reasons for this are:
- Lack of transmission and distribution networks to supply end-users (which are mainly forests and private companies such as golf resorts);
- Lower demand due to the financial downturn from 2008-2014;
- Cultural obstacles, such as convincing farmers to use recycled water.
There are about 79 medium and large wastewater treatment plants. In 2013, treated wastewater amounted to about 615MCM, or around 14% of the total water resources used.[7]
Cloud seeding
The UAE is one of the countries pioneering cloud seeding and artificial rainmaking in the MENA region. It spent 2 million dirhams (around $550,000) on cloud seeding operations in 2015.[8]
Cloud seeding usually takes place over the eastern mountain ranges on the border with Oman and aims to raise levels in aquifers and reservoirs in the area. However, some cloud seeding over the cities has also been carried out. Although this technique has proved its success in increasing the amount of precipitation, a detailed cost-benefit analysis needs to be carried out to ensure that it is a viable water source compared to options such as desalination or even water conservation campaigns. Table 1 shows the UAE’s water resources from 2002 and projections to 2050.
Table 1: Historical and projected water resources.[9]
| Quantity of water resources (MCM) | 2002 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2025 | 2050 |
| Surface run-off | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Average groundwater feed | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| Desalination | 720 | 945 | 1,488 | 2,342 | 3,688 | 5,806 | 11,612 |
| Treated water | 227 | 273 | 387 | 615 | 754 | 1,053 | 2,106 |
| Total | 1,222 | 1,493 | 2,150 | 3,232 | 4,717 | 7,134 | 13,993 |
[1] Mullah, M. -al, 2011. UAE State of Water Report. Second Arab Water Forum, Cairo, 20-23 November 2011. Available at www.slideshare.net/RuxandraLazarescu/p2-3mohamedal-mullauaestateofwaterreport, accessed 17 January 2017.
[2] ESCWA, 2003. Water scarcity in the Arab world. Population and development report. Beirut, Lebanon.
[3] Nouh, M., 2008. An Overview for the Water Resources of the United Arab Emirates. Proceedings of the 1st Technical Meeting of Muslim Water Researchers Cooperation, December 2008, Malaysia.
[4] WaterWorld, 13 October 2013. ‘Global desalination capacity growing substantially, finds study.’ Available at www.waterworld.com/articles/2013/10/global-desalination-capacity-tops-80-million-cubic-meters-per-day.html, accessed 30 March 2017.
[5] Ministry of Environment and Water, 2015. UAE State of Environment Report.
[6] The Gulf Intelligence, 10 April 2016. ‘Water-Food-Energy Nexus: Key lessons for the UAE?’ Available at www.thegulfintelligence.com/Docs.Viewer/0a2924e2-ed6a-47f6-aeae-affa938a7575/default.aspx, accessed 15 January 2017.
[7] Ministry of Environment and Water, 2015. UAE State of Environment Report.
[8] What’s On, 2016. ‘Dhs2 million spent on cloud seeding in the UAE last year’ Available at http://whatson.ae/dubai/2016/04/cloud-seeding-uae-in-2016/, accessed 22 January 2017.
[9] Adapted from Rizk, A., 2010. Water desalination in UAE: Problems and Solutions. Ajman Science and Technology University, KSA.