Contributors
Author: Dr. Ahmed Mahmoud. Wetsus, European centre of excellence for sustainable water technology.
Reviewer: Dr. Ahmed Mohamed, Geology Department, Assiut University.
Introduction
Water resources are regarded as one of the most crucial components of the environmental system and one of Egypt’s main foundations of growth. Given the scarcity of water resources and the rise in demand for them, it is imperative to protect and use all available resources to ensure their quality and good use. This is especially important because the current environment greatly increases the risk of pollution due to the rise in unplanned development and the ensuing industrial, agricultural, urban and tourist activities.
Geography and climate
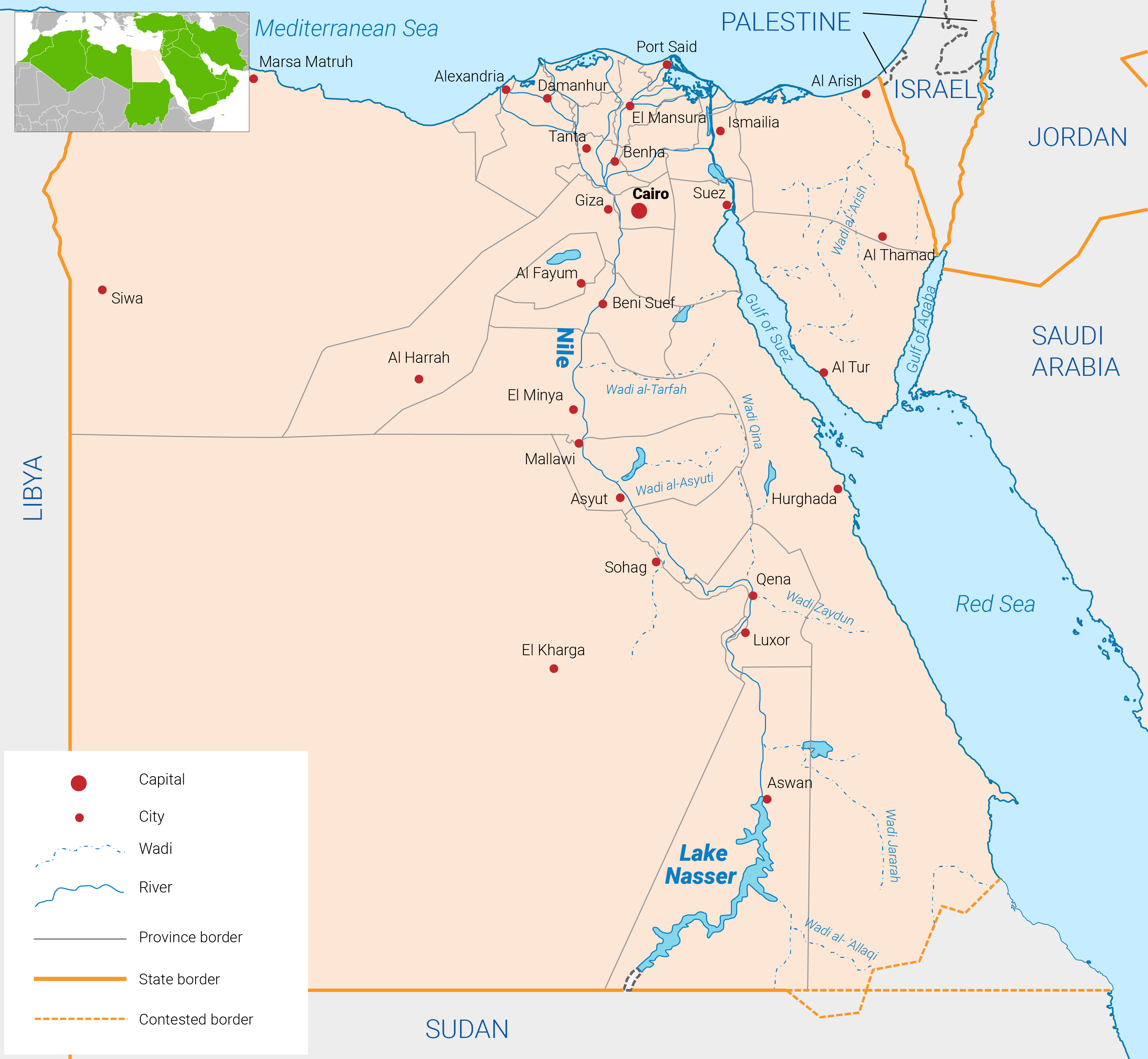
Egypt covers an area of approximately 1 million square kilometres (km2) and is located in the north-eastern part of the African continent. The Mediterranean Sea borders it to the north, Palestine, Israel and the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south and Libya to the west. Egypt’s vast desert plateau is only broken up by the Nile Valley and Nile Delta, which together account for only 4% of the country’s total area. The majority of the cultivated land is situated in the Nile Delta, along the River Nile‘s major branches and canals and close to its banks. There are no forests. Some 1.5 million hectares, or around 4% of the nation’s total land area, were under cultivation in 2013. This figure includes both arable land and perennial crops. Arable land accounts for approximately 1.1 million hectares, or 73% of the total cultivated area, and permanent crops occupy the remaining 0.4 million hectares.
Egypt’s climate is typically influenced by several variables, including geography and atmospheric pressure. This separates the country into various unique climate areas. Except for the northern regions, which are part of the temperate zone, Egypt is located in a dry tropical region. Its climate is similar to that of the Mediterranean, with hot, dry summers and mild winters with minimal rainfall, mainly on the north coast. Egypt’s winter season runs from December to March. The rains are accompanied by hot and cold wind disturbances, a decline in the amount of rain falling in the interior areas of Aswan, and occasional flooding from heavy rain that falls on the heights of South Sinai and the Red Sea highlands. Winter temperatures in Cairo can fall to 12°C while rising to 15°C in Alexandria and along the north coast and 18°C in the south where Luxor and Aswan are located. The lowest temperatures occur in December, January and February in the heights of the Sinai Peninsula, where the average is 5°C. The south of Egypt is also warmer due to the latitude effect.
The temperature reaches its highest range in the summer months of June, July and August, ranging from 28°C to 29°C in the north and from 40°C to 42°C in the south. Spring and autumn are mild transitional seasons. Autumn is the best season in terms of human comfort, especially November, when the country may get some early rainfall. Average highs in autumn range from 27°C in the north to 35°C in the south.
Population
Egypt’s rapid population growth and developing economy have strained already scarce water resources through dietary changes and increased domestic and industrial consumption. The population has grown substantially in recent decades, rising by 2.1% annually between 1989 and 2018. According to the Falkenmark indicator, the total renewable water resources per person was 628 cubic metres per year (m3/yr) in 2017, which was already below the threshold for water scarcity. Egypt also experienced major economic development from the middle of the 1950s.
Figure 1. Egypt’s population 1950-2020.1
Between 1989 and 2018, Egypt’s gross domestic product (GDP) expanded by 4.4% annually, although GDP per person only climbed by 2.3%. Along with this growth, domestic agricultural production has increased, as has water use for both urban and agricultural purposes.
Economy
According to the World Bank’s Egypt Economic Monitor report, Egypt’s economic growth is predicted to fall to 4.5% in fiscal year 2022-23 from 6.6% in fiscal year 2021-22. This is due to the Russia-Ukraine war overlapping with ongoing COVID-19-related interruptions.[2]
While vital sectors, particularly gas extractives, gain from increased global prices, as do the robust communications, agricultural and construction sectors, other industries, including manufacturing, are anticipated to perform below potential. At the same time, Egypt’s non-oil exports increased by 12% in the first ten months of 2022 to $30.4 billion, up from $27.1 billion in the same period in 2021, a $3.3 billion rise, according to data from the General Authority for Export and Import Control.[2]
[1] Worldometers. Population of Egypt. [cited 2023; Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/egypt-population/.
[2] NEWS, A. Egypt’s economic growth to decline to 4.5% in FY 2022-23: World Bank 2023; Available from: https://www.arabnews.com/node/2220261/business-economy.